Energy
Mapped: The World’s Largest State-Owned Oil Companies
View the full-resolution version of this infographic
Mapped: The World’s Largest State-Owned Oil Companies
View the high-resolution of the infographic by clicking here.
Oil is one of the world’s most important natural resources, playing a critical role in everything from transportation fuels to cosmetics.
For this reason, many governments choose to nationalize their supply of oil. This gives them a greater degree of control over their oil reserves as well as access to additional revenue streams. In practice, nationalization often involves the creation of a national oil company to oversee the country’s energy operations.
What are the world’s largest and most influential state-owned oil companies?
Editor’s Note: This post and infographic are intended to provide a broad summary of the state-owned oil industry. Due to variations in reporting and available information, the companies named do not represent a comprehensive index.
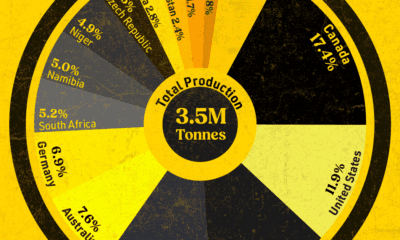
State-Owned Oil Companies by Revenue
National oil companies are a major force in the global energy sector, controlling approximately three-quarters of the Earth’s oil reserves.
As a result, many have found their place on the Fortune Global 500 list, a ranking of the world’s 500 largest companies by revenue.
| Country | Name | Fortune Global 500 Rank | 2019 Revenues |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 China | Sinopec Group | 2 | $443B |
| 🇨🇳 China | China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) | 4 | $379B |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | Saudi Aramco | 6 | $330B |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | Rosneft | 76 | $96B |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | Petrobras | 120 | $77B |
| 🇮🇳 India | Indian Oil Corporation (IOCL) | 151 | $69B |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | Petronas | 186 | $58B |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) | Not listed | $19B* |
| 🇻🇪 Venezuela | Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) | Not listed | $23B (2018) |
*Value of Iranian petroleum exports in 2019. Source: Fortune, Statista, OPEC
China is home to the two largest companies from this list, Sinopec Group and China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC). Both are involved in upstream and downstream oil operations, where upstream refers to exploration and extraction, and downstream refers to refining and distribution.
It’s worth noting that many of these companies are listed on public stock markets—Sinopec, for example, trades on exchanges located in Shanghai, Hong Kong, New York, and London. Going public can be an effective strategy for these companies as it allows them to raise capital for new projects, while also ensuring their governments maintain control. In the case of Sinopec, 68% of shares are held by the Chinese government.
Saudi Aramco was the latest national oil company to follow this strategy, putting up 1.5% of its business in a 2019 initial public offering (IPO). At roughly $8.53 per share, Aramco’s IPO raised $25.6 billion, making it one of the world’s largest IPOs in history.
Geopolitical Tensions
Because state-owned oil companies are directly tied to their governments, they can sometimes get caught in the crosshairs of geopolitical conflicts.
The disputed presidency of Nicolás Maduro, for example, has resulted in the U.S. imposing sanctions against Venezuela’s government, central bank, and national oil company, Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA). The pressure of these sanctions is proving to be particularly damaging, with PDVSA’s daily production in decline since 2016.
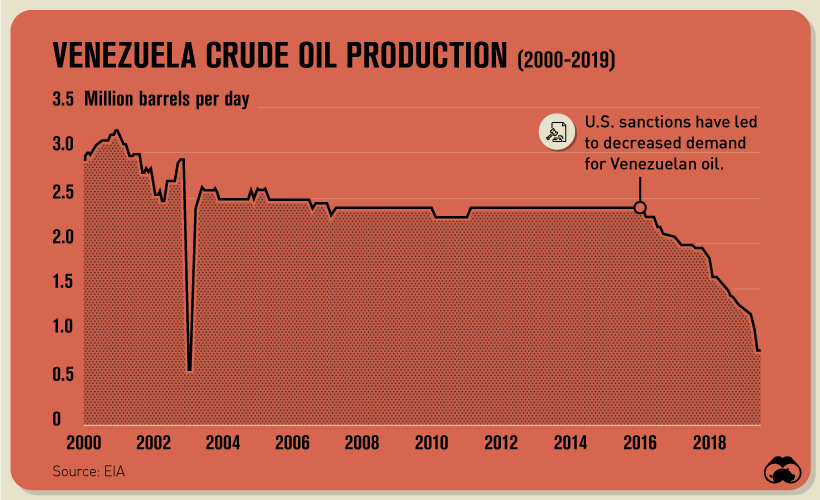
In a country for which oil comprises 95% of exports, Venezuela’s economic outlook is becoming increasingly dire. The final straw was drawn in August 2020 when the country’s last remaining oil rig suspended its operations.
Other national oil companies at the receiving end of American sanctions include Russia’s Rosneft and Iran’s National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC). Rosneft was sanctioned by the U.S. in 2020 for facilitating Venezuelan oil exports, while NIOC was targeted for providing financial support to Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, an entity designated as a foreign terrorist organization.
Climate Pressures
Like the rest of the fossil fuel industry, state-owned oil companies are highly exposed to the effects of climate change. This suggests that as time passes, many governments will need to find a balance between economic growth and environmental protection.
Brazil has already found itself in this dilemma as the country’s president, Jair Bolsonaro, has drawn criticism for his dismissive stance on climate change. In June 2020, a group of European investment firms representing $2 trillion in assets threatened to divest from Brazil if it did not do more to protect the Amazon rainforest.
These types of ultimatums may be an effective solution for driving climate action forward. In December 2020, Brazil’s national oil company, Petrobras, pledged a 25% reduction in carbon emissions by 2030. When asked about commitments further into the future, however, the company’s CEO appeared to be less enthusiastic.
That’s like a fad, to make promises for 2050. It’s like a magical year. On this side of the Atlantic we have a different view of climate change.
— Roberto Castello Branco, CEO, Petrobras
With its 2030 pledge, Petrobras joins a growing collection of state-owned oil companies that have made public climate commitments. Another example is Malaysia’s Petronas, which in November 2020, announced its intention to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Petronas is wholly owned by the Malaysian government and is the country’s only entry on the Fortune Global 500.
Challenges Lie Ahead
Between geopolitical conflicts, environmental concerns, and price fluctuations, state-owned oil companies are likely to face a much tougher environment in the decades to come.
For Petronas, achieving its 2050 climate commitments will require significant investment in cleaner forms of energy. The company has been involved in numerous solar energy projects across Asia and has stated its interests in hydrogen fuels.
Elsewhere, China’s national oil companies are dealing with a more near-term threat. In compliance with an executive order issued by the Trump Administration in November 2020, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) announced it would delist three of China’s state-run telecom companies. Analysts believe oil companies such as Sinopec could be delisted next, due to their ties with the Chinese military.
Energy
Charted: 4 Reasons Why Lithium Could Be the Next Gold Rush
Visual Capitalist has partnered with EnergyX to show why drops in prices and growing demand may make now the right time to invest in lithium.
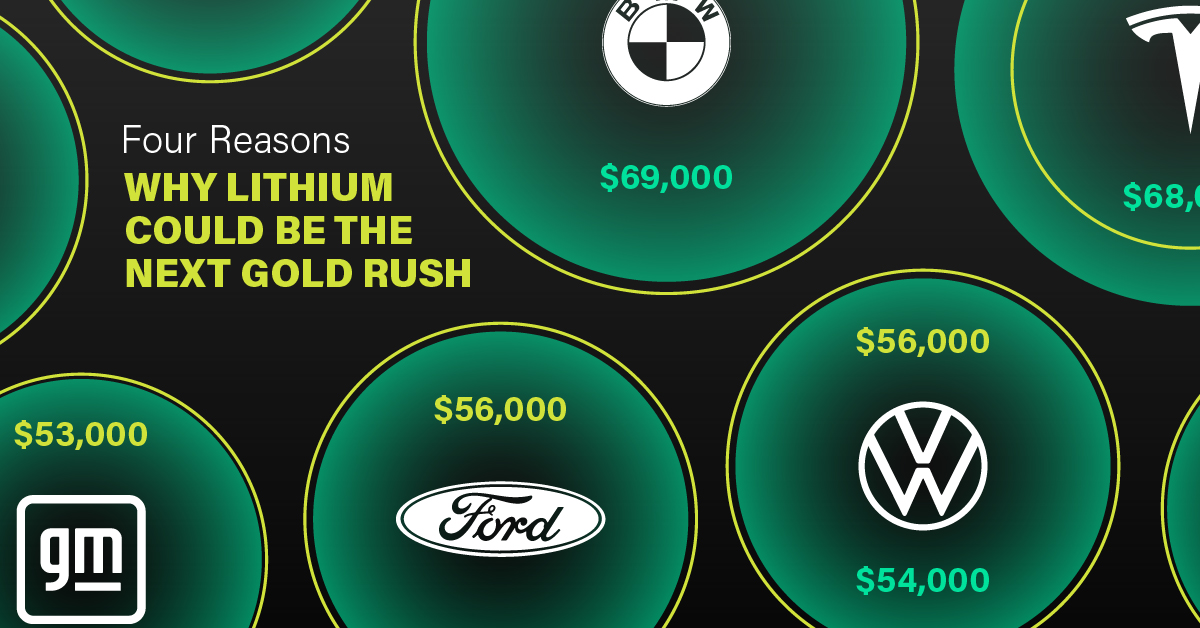
4 Reasons Why You Should Invest in Lithium
Lithium’s importance in powering EVs makes it a linchpin of the clean energy transition and one of the world’s most precious minerals.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnered with EnergyX to explore why now may be the time to invest in lithium.
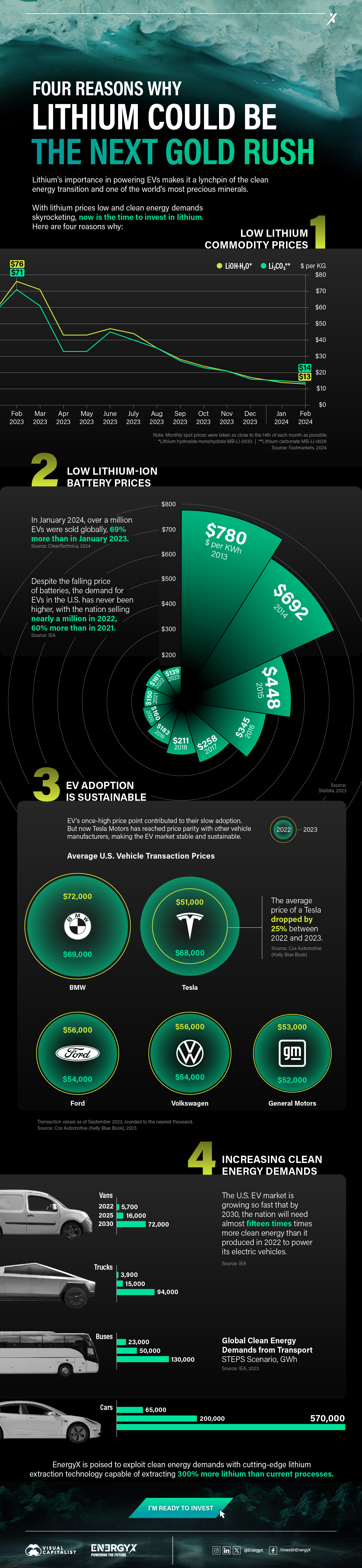
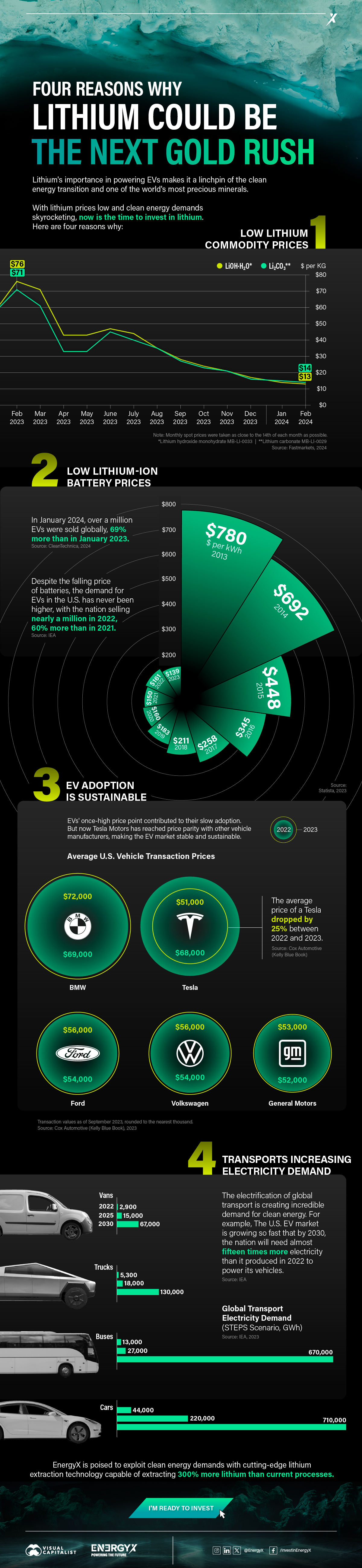
1. Lithium Prices Have Dropped
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating an investment is ensuring that the asset’s value is higher than its price would indicate. Lithium is integral to powering EVs, and, prices have fallen fast over the last year:
| Date | LiOH·H₂O* | Li₂CO₃** |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2023 | $76 | $71 |
| March 2023 | $71 | $61 |
| Apr 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| May 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| June 2023 | $47 | $45 |
| July 2023 | $44 | $40 |
| Aug 2023 | $35 | $35 |
| Sept 2023 | $28 | $27 |
| Oct 2023 | $24 | $23 |
| Nov 2023 | $21 | $21 |
| Dec 2023 | $17 | $16 |
| Jan 2024 | $14 | $15 |
| Feb 2024 | $13 | $14 |
Note: Monthly spot prices were taken as close to the 14th of each month as possible.
*Lithium hydroxide monohydrate MB-LI-0033
**Lithium carbonate MB-LI-0029
2. Lithium-Ion Battery Prices Are Also Falling
The drop in lithium prices is just one reason to invest in the metal. Increasing economies of scale, coupled with low commodity prices, have caused the cost of lithium-ion batteries to drop significantly as well.
In fact, BNEF reports that between 2013 and 2023, the price of a Li-ion battery dropped by 82%.
| Year | Price per KWh |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $139 |
| 2022 | $161 |
| 2021 | $150 |
| 2020 | $160 |
| 2019 | $183 |
| 2018 | $211 |
| 2017 | $258 |
| 2016 | $345 |
| 2015 | $448 |
| 2014 | $692 |
| 2013 | $780 |

3. EV Adoption is Sustainable
One of the best reasons to invest in lithium is that EVs, one of the main drivers behind the demand for lithium, have reached a price point similar to that of traditional vehicle.
According to the Kelly Blue Book, Tesla’s average transaction price dropped by 25% between 2022 and 2023, bringing it in line with many other major manufacturers and showing that EVs are a realistic transport option from a consumer price perspective.
| Manufacturer | September 2022 | September 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| BMW | $69,000 | $72,000 |
| Ford | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| Volkswagon | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| General Motors | $52,000 | $53,000 |
| Tesla | $68,000 | $51,000 |
4. Electricity Demand in Transport is Growing
As EVs become an accessible transport option, there’s an investment opportunity in lithium. But possibly the best reason to invest in lithium is that the IEA reports global demand for the electricity in transport could grow dramatically by 2030:
| Transport Type | 2022 | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buses 🚌 | 23,000 GWh | 50,000 GWh | 130,000 GWh |
| Cars 🚙 | 65,000 GWh | 200,000 GWh | 570,000 GWh |
| Trucks 🛻 | 4,000 GWh | 15,000 GWh | 94,000 GWh |
| Vans 🚐 | 6,000 GWh | 16,000 GWh | 72,000 GWh |
The Lithium Investment Opportunity
Lithium presents a potentially classic investment opportunity. Lithium and battery prices have dropped significantly, and recently, EVs have reached a price point similar to other vehicles. By 2030, the demand for clean energy, especially in transport, will grow dramatically.
With prices dropping and demand skyrocketing, now is the time to invest in lithium.
EnergyX is poised to exploit lithium demand with cutting-edge lithium extraction technology capable of extracting 300% more lithium than current processes.

-

 Lithium1 day ago
Lithium1 day agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
-

 Energy6 days ago
Energy6 days agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.
-

 Energy4 weeks ago
Energy4 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Oil Producers in 2023
Just three countries accounted for 40% of global oil production last year.
-
 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoHow Much Does the U.S. Depend on Russian Uranium?
Currently, Russia is the largest foreign supplier of nuclear power fuel to the U.S.
-
 Uranium2 months ago
Uranium2 months agoCharted: Global Uranium Reserves, by Country
We visualize the distribution of the world’s uranium reserves by country, with 3 countries accounting for more than half of total reserves.
-
 Energy2 months ago
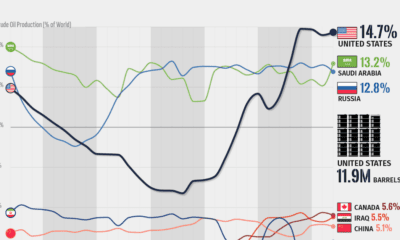
Energy2 months agoVisualizing the Rise of the U.S. as Top Crude Oil Producer
Over the last decade, the United States has established itself as the world’s top producer of crude oil, surpassing Saudi Arabia and Russia.
-

 Maps1 week ago
Maps1 week agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share